MCMC Model Comparison¶
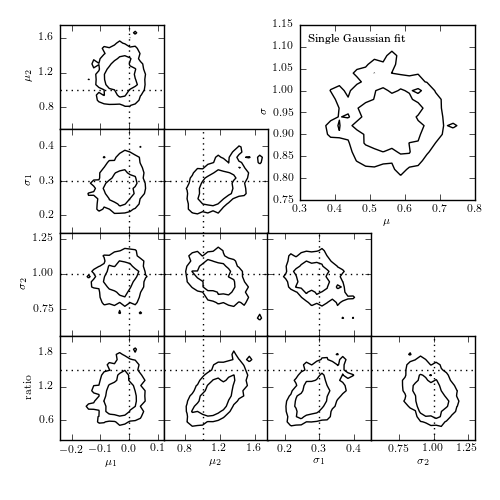
Figure 5.24
The top-right panel shows the posterior pdf for mu and sigma for a single Gaussian fit to the data shown in figure 5.23. The remaining panels show the projections of the five-dimensional pdf for a Gaussian mixture model with two components. Contours are based on a 10,000 point MCMC chain.
[-------------- 38% ] 3847 of 10000 complete in 0.5 sec
[-----------------75%-------- ] 7513 of 10000 complete in 1.0 sec
[-----------------100%-----------------] 10000 of 10000 complete in 1.3 sec
[ 2% ] 262 of 10000 complete in 0.5 sec
[- 5% ] 524 of 10000 complete in 1.0 sec
[-- 7% ] 781 of 10000 complete in 1.5 sec
[--- 10% ] 1031 of 10000 complete in 2.0 sec
[---- 12% ] 1282 of 10000 complete in 2.5 sec
[----- 15% ] 1533 of 10000 complete in 3.0 sec
[------ 17% ] 1780 of 10000 complete in 3.5 sec
[------- 20% ] 2026 of 10000 complete in 4.0 sec
[-------- 22% ] 2277 of 10000 complete in 4.5 sec
[--------- 25% ] 2525 of 10000 complete in 5.0 sec
[---------- 27% ] 2780 of 10000 complete in 5.5 sec
[----------- 30% ] 3030 of 10000 complete in 6.0 sec
[------------ 32% ] 3277 of 10000 complete in 6.5 sec
[------------- 35% ] 3527 of 10000 complete in 7.0 sec
[-------------- 37% ] 3780 of 10000 complete in 7.5 sec
[--------------- 40% ] 4022 of 10000 complete in 8.0 sec
[---------------- 42% ] 4272 of 10000 complete in 8.5 sec
[-----------------45% ] 4518 of 10000 complete in 9.0 sec
[-----------------47% ] 4769 of 10000 complete in 9.5 sec
[-----------------50% ] 5022 of 10000 complete in 10.0 sec
[-----------------52% ] 5278 of 10000 complete in 10.5 sec
[-----------------55% ] 5523 of 10000 complete in 11.0 sec
[-----------------57%- ] 5776 of 10000 complete in 11.5 sec
[-----------------60%-- ] 6021 of 10000 complete in 12.0 sec
[-----------------62%--- ] 6274 of 10000 complete in 12.5 sec
[-----------------65%---- ] 6520 of 10000 complete in 13.0 sec
[-----------------67%----- ] 6769 of 10000 complete in 13.5 sec
[-----------------70%------ ] 7013 of 10000 complete in 14.0 sec
[-----------------72%------- ] 7262 of 10000 complete in 14.5 sec
[-----------------75%-------- ] 7511 of 10000 complete in 15.0 sec
[-----------------77%--------- ] 7763 of 10000 complete in 15.5 sec
[-----------------80%---------- ] 8013 of 10000 complete in 16.0 sec
[-----------------82%----------- ] 8263 of 10000 complete in 16.5 sec
[-----------------85%------------ ] 8515 of 10000 complete in 17.0 sec
[-----------------87%------------- ] 8768 of 10000 complete in 17.5 sec
[-----------------90%-------------- ] 9016 of 10000 complete in 18.0 sec
[-----------------92%--------------- ] 9266 of 10000 complete in 18.5 sec
[-----------------95%---------------- ] 9514 of 10000 complete in 19.0 sec
[-----------------97%----------------- ] 9768 of 10000 complete in 19.5 sec
[-----------------100%-----------------] 10000 of 10000 complete in 20.0 sec
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy.special import gamma
from scipy.stats import norm
from sklearn.neighbors import BallTree
from astroML.density_estimation import GaussianMixture1D
from astroML.plotting import plot_mcmc
# hack to fix an import issue in older versions of pymc
import scipy
scipy.derivative = scipy.misc.derivative
import pymc
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
def get_logp(S, model):
"""compute log(p) given a pyMC model"""
M = pymc.MAP(model)
traces = np.array([S.trace(s)[:] for s in S.stochastics])
logp = np.zeros(traces.shape[1])
for i in range(len(logp)):
logp[i] = -M.func(traces[:, i])
return logp
def estimate_bayes_factor(traces, logp, r=0.05, return_list=False):
"""Estimate the bayes factor using the local density of points"""
D, N = traces.shape
# compute volume of a D-dimensional sphere of radius r
Vr = np.pi ** (0.5 * D) / gamma(0.5 * D + 1) * (r ** D)
# use neighbor count within r as a density estimator
bt = BallTree(traces.T)
count = bt.query_radius(traces.T, r=r, count_only=True)
BF = logp + np.log(N) + np.log(Vr) - np.log(count)
if return_list:
return BF
else:
p25, p50, p75 = np.percentile(BF, [25, 50, 75])
return p50, 0.7413 * (p75 - p25)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Generate the data
mu1_in = 0
sigma1_in = 0.3
mu2_in = 1
sigma2_in = 1
ratio_in = 1.5
N = 200
np.random.seed(10)
gm = GaussianMixture1D([mu1_in, mu2_in],
[sigma1_in, sigma2_in],
[ratio_in, 1])
x_sample = gm.sample(N)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Set up pyMC model: single gaussian
# 2 parameters: (mu, sigma)
M1_mu = pymc.Uniform('M1_mu', -5, 5, value=0)
M1_log_sigma = pymc.Uniform('M1_log_sigma', -10, 10, value=0)
@pymc.deterministic
def M1_sigma(M1_log_sigma=M1_log_sigma):
return np.exp(M1_log_sigma)
@pymc.deterministic
def M1_tau(M1_sigma=M1_sigma):
return 1. / M1_sigma ** 2
M1 = pymc.Normal('M1', M1_mu, M1_tau, observed=True, value=x_sample)
model1 = dict(M1_mu=M1_mu, M1_log_sigma=M1_log_sigma,
M1_sigma=M1_sigma,
M1_tau=M1_tau, M1=M1)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Set up pyMC model: double gaussian
# 5 parameters: (mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2, ratio)
def doublegauss_like(x, mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2, ratio):
"""log-likelihood for double gaussian"""
r1 = ratio / (1. + ratio)
r2 = 1 - r1
L = r1 * norm(mu1, sigma1).pdf(x) + r2 * norm(mu2, sigma2).pdf(x)
L[L == 0] = 1E-16 # prevent divide-by-zero error
logL = np.log(L).sum()
if np.isinf(logL):
raise pymc.ZeroProbability
else:
return logL
def rdoublegauss(mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2, ratio, size=None):
"""random variable from double gaussian"""
r1 = ratio / (1. + ratio)
r2 = 1 - r1
R = np.asarray(np.random.random(size))
Rshape = R.shape
R = np.atleast1d(R)
mask1 = (R < r1)
mask2 = ~mask1
N1 = mask1.sum()
N2 = R.size - N1
R[mask1] = norm(mu1, sigma1).rvs(N1)
R[mask2] = norm(mu2, sigma2).rvs(N2)
return R.reshape(Rshape)
DoubleGauss = pymc.stochastic_from_dist('doublegauss',
logp=doublegauss_like,
random=rdoublegauss,
dtype=np.float,
mv=True)
# set up our Stochastic variables, mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2, ratio
M2_mu1 = pymc.Uniform('M2_mu1', -5, 5, value=0)
M2_mu2 = pymc.Uniform('M2_mu2', -5, 5, value=1)
M2_log_sigma1 = pymc.Uniform('M2_log_sigma1', -10, 10, value=0)
M2_log_sigma2 = pymc.Uniform('M2_log_sigma2', -10, 10, value=0)
@pymc.deterministic
def M2_sigma1(M2_log_sigma1=M2_log_sigma1):
return np.exp(M2_log_sigma1)
@pymc.deterministic
def M2_sigma2(M2_log_sigma2=M2_log_sigma2):
return np.exp(M2_log_sigma2)
M2_ratio = pymc.Uniform('M2_ratio', 1E-3, 1E3, value=1)
M2 = DoubleGauss('M2', M2_mu1, M2_mu2, M2_sigma1, M2_sigma2, M2_ratio,
observed=True, value=x_sample)
model2 = dict(M2_mu1=M2_mu1, M2_mu2=M2_mu2,
M2_log_sigma1=M2_log_sigma1, M2_log_sigma2=M2_log_sigma2,
M2_sigma1=M2_sigma1, M2_sigma2=M2_sigma2,
M2_ratio=M2_ratio, M2=M2)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Set up MCMC sampling
def compute_MCMC_models(Niter=10000, burn=1000, rseed=0):
pymc.numpy.random.seed(rseed)
S1 = pymc.MCMC(model1)
S1.sample(iter=Niter, burn=burn)
trace1 = np.vstack([S1.trace('M1_mu')[:],
S1.trace('M1_sigma')[:]])
logp1 = get_logp(S1, model1)
S2 = pymc.MCMC(model2)
S2.sample(iter=Niter, burn=burn)
trace2 = np.vstack([S2.trace('M2_mu1')[:],
S2.trace('M2_mu2')[:],
S2.trace('M2_sigma1')[:],
S2.trace('M2_sigma2')[:],
S2.trace('M2_ratio')[:]])
logp2 = get_logp(S2, model2)
return trace1, logp1, trace2, logp2
trace1, logp1, trace2, logp2 = compute_MCMC_models()
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Compute Odds ratio with density estimation technique
BF1, dBF1 = estimate_bayes_factor(trace1, logp1, r=0.02)
BF2, dBF2 = estimate_bayes_factor(trace2, logp2, r=0.05)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Plot the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
labels = [r'$\mu_1$',
r'$\mu_2$',
r'$\sigma_1$',
r'$\sigma_2$',
r'${\rm ratio}$']
true_values = [mu1_in,
mu2_in,
sigma1_in,
sigma2_in,
ratio_in]
limits = [(-0.24, 0.12),
(0.55, 1.75),
(0.15, 0.45),
(0.55, 1.3),
(0.25, 2.1)]
# we assume mu1 < mu2, but the results may be switched
# due to the symmetry of the problem. If so, switch back
if np.median(trace2[0]) > np.median(trace2[1]):
trace2 = trace2[[1, 0, 3, 2, 4], :]
N2_norm_mu = N2.mu[N2.M2_mu2, N2.M2_mu1,
N2.M2_sigma2, N2.M2_sigma1, N2.M2_ratio]
N2_norm_Sig = N2.C[N2.M2_mu2, N2.M2_mu1,
N2.M2_sigma2, N2.M2_sigma1, N2.M2_ratio]
# Plot the simple 2-component model
ax, = plot_mcmc(trace1, fig=fig, bounds=[0.6, 0.6, 0.95, 0.95],
limits=[(0.3, 0.8), (0.75, 1.15)],
labels=[r'$\mu$', r'$\sigma$'], colors='k')
ax.text(0.05, 0.95, "Single Gaussian fit", va='top', ha='left',
transform=ax.transAxes)
# Plot the 5-component model
ax_list = plot_mcmc(trace2, limits=limits, labels=labels,
true_values=true_values, fig=fig,
bounds=(0.12, 0.12, 0.95, 0.95),
colors='k')
for ax in ax_list:
for axis in [ax.xaxis, ax.yaxis]:
axis.set_major_locator(plt.MaxNLocator(4))
plt.show()
