MCMC for the Cauchy distribution¶
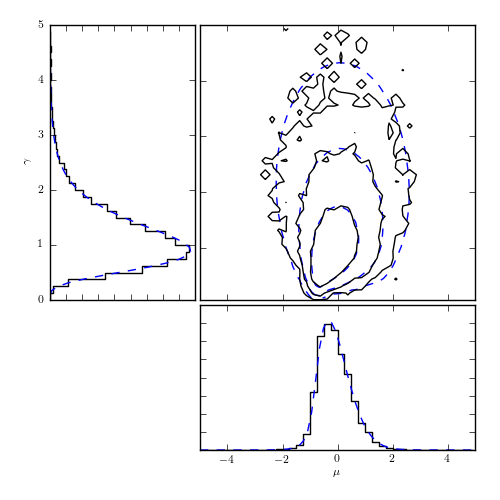
Figure 5.22
Markov chain monte carlo (MCMC) estimates of the posterior pdf for parameters describing the Cauchy distribution. The data are the same as those used in figure 5.10: the dashed curves in the top-right panel show the results of direct computation on a regular grid from that diagram. The solid curves are the corresponding MCMC estimates using 10,000 sample points. The left and the bottom panels show marginalized distributions.
[---- 10% ] 5430 of 50000 complete in 0.5 sec
[------- 19% ] 9540 of 50000 complete in 1.0 sec
[---------- 27% ] 13655 of 50000 complete in 1.5 sec
[------------- 35% ] 17753 of 50000 complete in 2.0 sec
[---------------- 43% ] 21933 of 50000 complete in 2.5 sec
[-----------------52% ] 26047 of 50000 complete in 3.0 sec
[-----------------60%--- ] 30355 of 50000 complete in 3.5 sec
[-----------------68%------ ] 34487 of 50000 complete in 4.0 sec
[-----------------77%--------- ] 38706 of 50000 complete in 4.5 sec
[-----------------85%------------ ] 42909 of 50000 complete in 5.0 sec
[-----------------94%--------------- ] 47135 of 50000 complete in 5.5 sec
[-----------------100%-----------------] 50000 of 50000 complete in 5.9 sec
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import cauchy
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from astroML.plotting.mcmc import convert_to_stdev
# this fixes a problem when using older versions of pymc with newer
# versions of scipy
import scipy
scipy.derivative = scipy.misc.derivative
import pymc
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
def cauchy_logL(xi, sigma, mu):
"""Equation 5.74: cauchy likelihood"""
xi = np.asarray(xi)
n = xi.size
shape = np.broadcast(sigma, mu).shape
xi = xi.reshape(xi.shape + tuple([1 for s in shape]))
return ((n - 1) * np.log(sigma)
- np.sum(np.log(sigma ** 2 + (xi - mu) ** 2), 0))
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Draw the sample from a Cauchy distribution
np.random.seed(44)
mu_0 = 0
gamma_0 = 2
xi = cauchy(mu_0, gamma_0).rvs(10)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Perform MCMC:
# set up our Stochastic variables, mu and gamma
mu = pymc.Uniform('mu', -5, 5)
log_gamma = pymc.Uniform('log_gamma', -10, 10, value=0)
@pymc.deterministic
def gamma(log_gamma=log_gamma):
return np.exp(log_gamma)
# set up our observed variable x
x = pymc.Cauchy('x', mu, gamma, observed=True, value=xi)
# set up our model dictionary
model = dict(mu=mu, log_gamma=log_gamma, gamma=gamma, x=x)
# perform the MCMC
S = pymc.MCMC(model)
S.sample(iter=50000, burn=5000)
# extract the traces we're interested in
trace_mu = S.trace('mu')[:]
trace_gamma = S.trace('gamma')[:]
# compute histogram of results to plot below
L_MCMC, mu_bins, gamma_bins = np.histogram2d(trace_mu, trace_gamma,
bins=(np.linspace(-5, 5, 41),
np.linspace(0, 5, 41)))
L_MCMC[L_MCMC == 0] = 1E-16 # prevents zero-division errors
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Compute likelihood analytically for comparison
mu = np.linspace(-5, 5, 70)
gamma = np.linspace(0.1, 5, 70)
logL = cauchy_logL(xi, gamma[:, np.newaxis], mu)
logL -= logL.max()
p_mu = np.exp(logL).sum(0)
p_mu /= p_mu.sum() * (mu[1] - mu[0])
p_gamma = np.exp(logL).sum(1)
p_gamma /= p_gamma.sum() * (gamma[1] - gamma[0])
hist_mu, bins_mu = np.histogram(trace_mu, bins=mu_bins, normed=True)
hist_gamma, bins_gamma = np.histogram(trace_gamma, bins=gamma_bins,
normed=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# plot the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
# first axis: likelihood contours
ax1 = fig.add_axes((0.4, 0.4, 0.55, 0.55))
ax1.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax1.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax1.contour(mu, gamma, convert_to_stdev(logL),
levels=(0.683, 0.955, 0.997),
colors='b', linestyles='dashed')
ax1.contour(0.5 * (mu_bins[:-1] + mu_bins[1:]),
0.5 * (gamma_bins[:-1] + gamma_bins[1:]),
convert_to_stdev(np.log(L_MCMC.T)),
levels=(0.683, 0.955, 0.997),
colors='k')
# second axis: marginalized over mu
ax2 = fig.add_axes((0.1, 0.4, 0.29, 0.55))
ax2.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax2.plot(hist_gamma, 0.5 * (bins_gamma[1:] + bins_gamma[:-1]
- bins_gamma[1] + bins_gamma[0]),
'-k', drawstyle='steps')
ax2.plot(p_gamma, gamma, '--b')
ax2.set_ylabel(r'$\gamma$')
ax2.set_ylim(0, 5)
# third axis: marginalized over gamma
ax3 = fig.add_axes((0.4, 0.1, 0.55, 0.29))
ax3.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
ax3.plot(0.5 * (bins_mu[1:] + bins_mu[:-1]), hist_mu,
'-k', drawstyle='steps-mid')
ax3.plot(mu, p_mu, '--b')
ax3.set_xlabel(r'$\mu$')
plt.xlim(-5, 5)
plt.show()
