Cross Validation Examples: Part 4¶
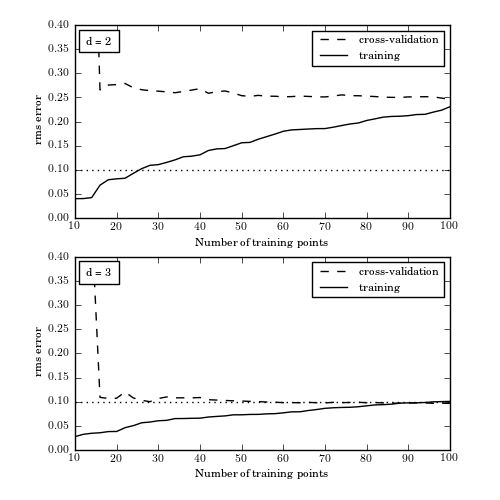
Figure 8.15
The learning curves for the data given by eq. 8.75, with d = 2 and d = 3. Both models have high variance for a few data points, visible in the spread between training and validation error. As the number of points increases, it is clear that d = 2 is a high-bias model which cannot be improved simply by adding training points.
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import ticker
from matplotlib.patches import FancyArrow
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Define our functional form
def func(x, dy=0.1):
return np.random.normal(np.sin(x) * x, dy)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# select the (noisy) data
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.linspace(0, 3, 22)[1:-1]
dy = 0.1
y = func(x, dy)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Select the cross-validation points
np.random.seed(1)
x_cv = 3 * np.random.random(20)
y_cv = func(x_cv)
x_fit = np.linspace(0, 3, 1000)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Fourth figure: plot errors as a function of training set size
np.random.seed(0)
x = 3 * np.random.random(100)
y = func(x)
np.random.seed(1)
x_cv = 3 * np.random.random(100)
y_cv = func(x_cv)
Nrange = np.arange(10, 101, 2)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.15, top=0.95)
for subplot, d in zip([211, 212], [2, 3]):
ax = fig.add_subplot(subplot)
training_err = np.zeros(Nrange.shape)
crossval_err = np.zeros(Nrange.shape)
for j, N in enumerate(Nrange):
p = np.polyfit(x[:N], y[:N], d)
training_err[j] = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.polyval(p, x[:N])
- y[:N]) ** 2) / len(y))
crossval_err[j] = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.polyval(p, x_cv)
- y_cv) ** 2) / len(y_cv))
ax.plot(Nrange, crossval_err, '--k', label='cross-validation')
ax.plot(Nrange, training_err, '-k', label='training')
ax.plot(Nrange, 0.1 * np.ones(Nrange.shape), ':k')
ax.legend(loc=1)
ax.text(0.03, 0.94, "d = %i" % d, transform=ax.transAxes,
ha='left', va='top', bbox=dict(ec='k', fc='w', pad=10))
ax.set_ylim(0, 0.4)
ax.set_xlabel('Number of training points')
ax.set_ylabel('rms error')
plt.show()
