Total Least Squares Figure¶
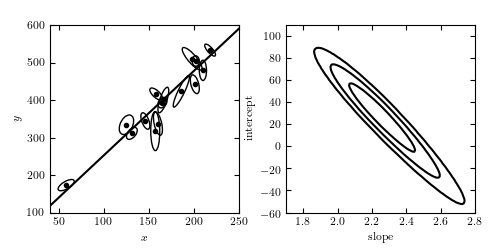
Figure 8.6
A linear fit to data with correlated errors in x and y. In the literature, this is often referred to as total least squares or errors-in-variables fitting. The left panel shows the lines of best fit; the right panel shows the likelihood contours in slope/intercept space. The points are the same set used for the examples in Hogg, Bovy & Lang 2010.
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 55.711167
Iterations: 88
Function evaluations: 164
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from scipy import optimize
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
from astroML.linear_model import TLS_logL
from astroML.plotting.mcmc import convert_to_stdev
from astroML.datasets import fetch_hogg2010test
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
if "setup_text_plots" not in globals():
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Define some convenience functions
# translate between typical slope-intercept representation,
# and the normal vector representation
def get_m_b(beta):
b = np.dot(beta, beta) / beta[1]
m = -beta[0] / beta[1]
return m, b
def get_beta(m, b):
denom = (1 + m * m)
return np.array([-b * m / denom, b / denom])
# compute the ellipse pricipal axes and rotation from covariance
def get_principal(sigma_x, sigma_y, rho_xy):
sigma_xy2 = rho_xy * sigma_x * sigma_y
alpha = 0.5 * np.arctan2(2 * sigma_xy2,
(sigma_x ** 2 - sigma_y ** 2))
tmp1 = 0.5 * (sigma_x ** 2 + sigma_y ** 2)
tmp2 = np.sqrt(0.25 * (sigma_x ** 2 - sigma_y ** 2) ** 2 + sigma_xy2 ** 2)
return np.sqrt(tmp1 + tmp2), np.sqrt(tmp1 - tmp2), alpha
# plot ellipses
def plot_ellipses(x, y, sigma_x, sigma_y, rho_xy, factor=2, ax=None):
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
sigma1, sigma2, alpha = get_principal(sigma_x, sigma_y, rho_xy)
for i in range(len(x)):
ax.add_patch(Ellipse((x[i], y[i]),
factor * sigma1[i], factor * sigma2[i],
alpha[i] * 180. / np.pi,
fc='none', ec='k'))
#------------------------------------------------------------
# We'll use the data from table 1 of Hogg et al. 2010
data = fetch_hogg2010test()
data = data[5:] # no outliers
x = data['x']
y = data['y']
sigma_x = data['sigma_x']
sigma_y = data['sigma_y']
rho_xy = data['rho_xy']
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Find best-fit parameters
X = np.vstack((x, y)).T
dX = np.zeros((len(x), 2, 2))
dX[:, 0, 0] = sigma_x ** 2
dX[:, 1, 1] = sigma_y ** 2
dX[:, 0, 1] = dX[:, 1, 0] = rho_xy * sigma_x * sigma_y
min_func = lambda beta: -TLS_logL(beta, X, dX)
beta_fit = optimize.fmin(min_func,
x0=[-1, 1])
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Plot the data and fits
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 2.5))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.1, right=0.95, wspace=0.25,
bottom=0.15, top=0.9)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# first let's visualize the data
ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
ax.scatter(x, y, c='k', s=9)
plot_ellipses(x, y, sigma_x, sigma_y, rho_xy, ax=ax)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# plot the best-fit line
m_fit, b_fit = get_m_b(beta_fit)
x_fit = np.linspace(0, 300, 10)
ax.plot(x_fit, m_fit * x_fit + b_fit, '-k')
ax.set_xlim(40, 250)
ax.set_ylim(100, 600)
ax.set_xlabel('$x$')
ax.set_ylabel('$y$')
#------------------------------------------------------------
# plot the likelihood contour in m, b
ax = fig.add_subplot(122)
m = np.linspace(1.7, 2.8, 100)
b = np.linspace(-60, 110, 100)
logL = np.zeros((len(m), len(b)))
for i in range(len(m)):
for j in range(len(b)):
logL[i, j] = TLS_logL(get_beta(m[i], b[j]), X, dX)
ax.contour(m, b, convert_to_stdev(logL.T),
levels=(0.683, 0.955, 0.997),
colors='k')
ax.set_xlabel('slope')
ax.set_ylabel('intercept')
ax.set_xlim(1.7, 2.8)
ax.set_ylim(-60, 110)
plt.show()
