Regularized Regression Example¶
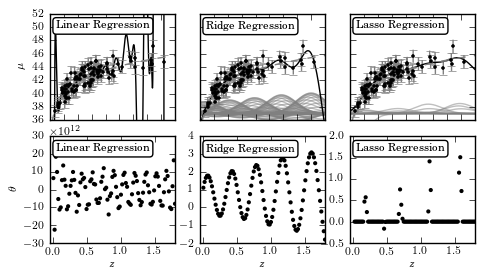
Figure 8.4
Regularized regression for the same sample as Fig. 8.2. Here we use Gaussian basis function regression with a Gaussian of width sigma = 0.2 centered at 100 regular intervals between 0 < z < 2. The lower panels show the best-fit weights as a function of basis function position. The left column shows the results with no regularization: the basis function weights w are on the order of 108, and overfitting is evident. The middle column shows ridge regression (L2 regularization) with alpha = 0.005, and the right column shows LASSO regression (L1 regularization) with alpha = 0.005. All three methods are fit without the bias term (intercept).
WARNING: Objective did not converge. You might want to increase the number of iterations [sklearn.linear_model.coordinate_descent]
# Author: Jake VanderPlas
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import lognorm
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, Ridge, Lasso
from astroML.cosmology import Cosmology
from astroML.datasets import generate_mu_z
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# generate data
np.random.seed(0)
z_sample, mu_sample, dmu = generate_mu_z(100, random_state=0)
cosmo = Cosmology()
z = np.linspace(0.01, 2, 1000)
mu = np.asarray(map(cosmo.mu, z))
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Manually convert data to a gaussian basis
# note that we're ignoring errors here, for the sake of example.
def gaussian_basis(x, mu, sigma):
return np.exp(-0.5 * ((x - mu) / sigma) ** 2)
centers = np.linspace(0, 1.8, 100)
widths = 0.2
X = gaussian_basis(z_sample[:, np.newaxis], centers, widths)
#------------------------------------------------------------
# Set up the figure to plot the results
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 2.7))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.1, right=0.95,
bottom=0.1, top=0.95,
hspace=0.15, wspace=0.2)
classifier = [LinearRegression, Ridge, Lasso]
kwargs = [dict(), dict(alpha=0.005), dict(alpha=0.001)]
labels = ['Linear Regression', 'Ridge Regression', 'Lasso Regression']
for i in range(3):
clf = classifier[i](fit_intercept=True, **kwargs[i])
clf.fit(X, mu_sample)
w = clf.coef_
fit = clf.predict(gaussian_basis(z[:, None], centers, widths))
# plot fit
ax = fig.add_subplot(231 + i)
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
# plot curves for regularized fits
if i == 0:
ax.set_ylabel('$\mu$')
else:
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(plt.NullFormatter())
curves = 37 + w * gaussian_basis(z[:, np.newaxis], centers, widths)
curves = curves[:, abs(w) > 0.01]
ax.plot(z, curves,
c='gray', lw=1, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot(z, fit, '-k')
ax.plot(z, mu, '--', c='gray')
ax.errorbar(z_sample, mu_sample, dmu, fmt='.k', ecolor='gray', lw=1, ms=4)
ax.set_xlim(0.001, 1.8)
ax.set_ylim(36, 52)
ax.text(0.05, 0.93, labels[i],
ha='left', va='top',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', ec='k', fc='w'),
transform=ax.transAxes)
# plot weights
ax = plt.subplot(234 + i)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(0.5))
ax.set_xlabel('$z$')
if i == 0:
ax.set_ylabel(r'$\theta$')
w *= 1E-12
ax.text(0, 1.01, r'$\rm \times 10^{12}$',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.scatter(centers, w, s=9, lw=0, c='k')
ax.set_xlim(-0.05, 1.8)
if i == 1:
ax.set_ylim(-2, 4)
elif i == 2:
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, 2)
ax.text(0.05, 0.93, labels[i],
ha='left', va='top',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', ec='k', fc='w'),
transform=ax.transAxes)
plt.show()
