Gaussian Distribution with Gaussian Errors¶
Figure 5.25
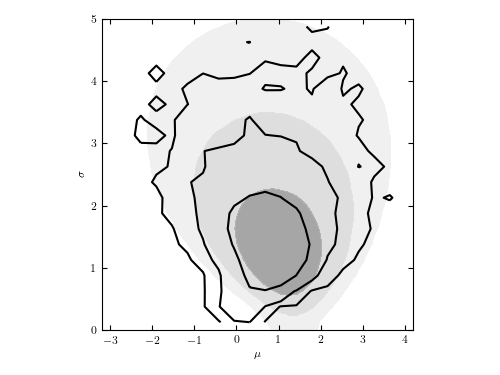
The posterior pdf for mu and sigma for a Gaussian distribution with heteroscedastic errors. This is the same data set as used in figure 5.7, but here each measurement error is assumed unknown, treated as a model parameter with a scale-invariant prior, and marginalized over to obtain the distribution of mu and sigma shown by contours. For comparison, the posterior pdf from figure 5.7 is shown by shaded contours.
# Author: Jake VanderPlas (adapted to PyMC3 by Brigitta Sipocz)
# License: BSD
# The figure produced by this code is published in the textbook
# "Statistics, Data Mining, and Machine Learning in Astronomy" (2013)
# For more information, see http://astroML.github.com
# To report a bug or issue, use the following forum:
# https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/astroml-general
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import pymc3 as pm
from astroML.plotting.mcmc import convert_to_stdev
from astroML.plotting import plot_mcmc
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# This function adjusts matplotlib settings for a uniform feel in the textbook.
# Note that with usetex=True, fonts are rendered with LaTeX. This may
# result in an error if LaTeX is not installed on your system. In that case,
# you can set usetex to False.
if "setup_text_plots" not in globals():
from astroML.plotting import setup_text_plots
setup_text_plots(fontsize=8, usetex=True)
def gaussgauss_logL(xi, ei, mu, sigma):
"""Equation 5.22: gaussian likelihood"""
ndim = len(np.broadcast(sigma, mu).shape)
xi = xi.reshape(xi.shape + tuple(ndim * [1]))
ei = ei.reshape(ei.shape + tuple(ndim * [1]))
s2_e2 = sigma ** 2 + ei ** 2
return -0.5 * np.sum(np.log(s2_e2) + (xi - mu) ** 2 / s2_e2, 0)
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Select the data
np.random.seed(5)
mu_true = 1.
sigma_true = 1.
N = 10
ei = 3 * np.random.random(N)
xi = np.random.normal(mu_true, np.sqrt(sigma_true ** 2 + ei ** 2))
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Set up MCMC for our model parameters: (mu, sigma, ei)
with pm.Model() as model:
mu = pm.Uniform('mu', -10, 10)
log_sigma = pm.Uniform('log_sigma', -10, 10)
log_error = pm.Uniform('log_error', -10, 10, shape=(N,))
def sigma_m(log_sigma, log_error):
return np.sqrt(np.exp(log_sigma) ** 2 + np.exp(log_error)**2)
x = pm.Normal('x', mu=mu, sd=sigma_m(log_sigma, log_error), observed=xi)
# perform the MCMC sampling
trace = pm.sample(draws=4500, tune=1500)
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Extract the MCMC traces
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 3.75))
ax, = plot_mcmc([trace['mu'], np.exp(trace['log_sigma'])], fig=fig,
limits=[(-3.2, 4.2), (0, 5)],
bounds=(0.08, 0.12, 0.95, 0.95),
labels=(r'$\mu$', r'$\sigma$'),
levels=[0.683, 0.955, 0.997],
colors='k')
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Compute and plot likelihood with known ei for comparison
# (Same as fig_likelihood_gaussgauss)
sigma = np.linspace(0.01, 5, 41)
mu = np.linspace(-3.2, 4.2, 41)
logL = gaussgauss_logL(xi, ei, mu, sigma[:, np.newaxis])
logL -= logL.max()
im = ax.contourf(mu, sigma, convert_to_stdev(logL),
levels=(0, 0.683, 0.955, 0.997),
cmap=plt.cm.binary_r, alpha=0.5)
im.set_clim(0, 1.1)
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\mu$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'$\sigma$')
ax.set_xlim(-3.2, 4.2)
ax.set_ylim(0, 5)
ax.set_aspect(1. / ax.get_data_ratio())
plt.show()
